Will Quantum Computers Ever Supplant Traditional Computing?
Written on
Chapter 1: The Limits of Traditional Computing
As technology continues to advance, the performance of traditional computers is bound to face limits due to fundamental physical constraints. Currently, enhancements in performance are largely achieved through miniaturization, with transistors being shrunk to fit more logic components within a cubic centimeter.
Nevertheless, this trend of miniaturization cannot persist indefinitely. By the end of 2023 and into 2024, we expect to see processors manufactured using a 3-nanometer technology, where the smallest size of an element measures 3 nanometers. For context, a silicon atom, commonly utilized in chip production, is approximately 0.21 nanometers in size. We are nearing the limits imposed by the atomic structure of materials.
In this context, many experts are turning their attention to quantum computers as a potential alternative to conventional electronic systems.
Section 1.1: Understanding Quantum Computers
In essence, a quantum computer is a device that leverages principles of quantum mechanics, such as superposition and entanglement, to store and process information.
In this realm, data is encoded in quantum bits, or qubits.
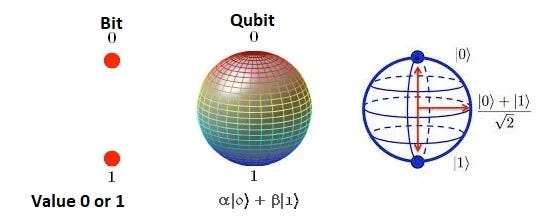
While a traditional bit can exist in one of two states—0 or 1—a qubit can be in a state of superposition, represented as ?|0?+?|1?, where ? and ? denote the probabilities of measuring the qubit in either state. This unique property enables quantum computers to process numerous possibilities simultaneously, offering a significant edge over classical systems for specific problem types.
Section 1.2: The Speed Debate
A prevalent myth is that quantum computers operate at a much higher speed than their traditional counterparts. However, this is misleading; current quantum systems are generally thousands to tens of thousands of times slower than conventional computers.

Nonetheless, there are particular classes of problems where quantum computers can dramatically outperform classical ones due to their inherent structure. A prime example is integer factorization, especially for very large numbers. This problem is crucial for modern encryption methods, which rely on the difficulty of breaking down massive integers.

The rise of efficient methods for integer factorization presents a threat to various encryption algorithms, impacting electronic security systems and cryptocurrency holders alike.
Chapter 2: The Path Forward
A pivotal aspect of advancing quantum computing is achieving fault tolerance. The information in qubits is susceptible to decoherence—interactions with surrounding particles that can disrupt coherence.
The Quantum Threshold Theorem provides a glimmer of hope: it suggests that if we can develop a quantum scheme with a high enough precision, we could accurately simulate a quantum computer.
Opinions on the feasibility of this breakthrough vary widely. While some experts are optimistic, others approach it with skepticism.

Even if we achieve the necessary precision for quantum chips and develop reliable quantum systems, it's unlikely they will fully replace conventional digital computers. The two types of computers cater to different applications. Quantum systems don't have advantages for problems where efficient algorithms already exist.
The most probable scenario is the emergence of hybrid systems, combining traditional CPUs with quantum coprocessors to tackle complex tasks, like large integer factorization.
For further insights on the evolution of quantum computing, check out the video titled "Quantum Computing 2024 Update."
Also, don’t miss the video "Why Quantum Computers Will Break Reality" for a deeper understanding of the implications of this technology.
Support our content creation journey by becoming a member for just $5 a month, and feel free to subscribe for more articles on space and technology!