Title: The Vital Role of Plankton and Our Responsibility
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Plankton
Recently, I stumbled upon some astonishing facts about plankton that compelled me to share this information. It’s crucial for the world to gain a deeper understanding of these organisms.
Did you know that phytoplankton are responsible for producing over half of the oxygen we breathe? These minuscule organisms, largely invisible to the naked eye, play a significant role in sustaining life on Earth.
To start, it’s essential to differentiate between the two primary types of plankton. Phytoplankton (plant-like plankton) are photosynthetic entities that convert sunlight and carbon dioxide into energy. Conversely, zooplankton (animal-like plankton) rely on phytoplankton for food, forming a crucial link in the marine food web, especially as prey for majestic creatures such as right whales.
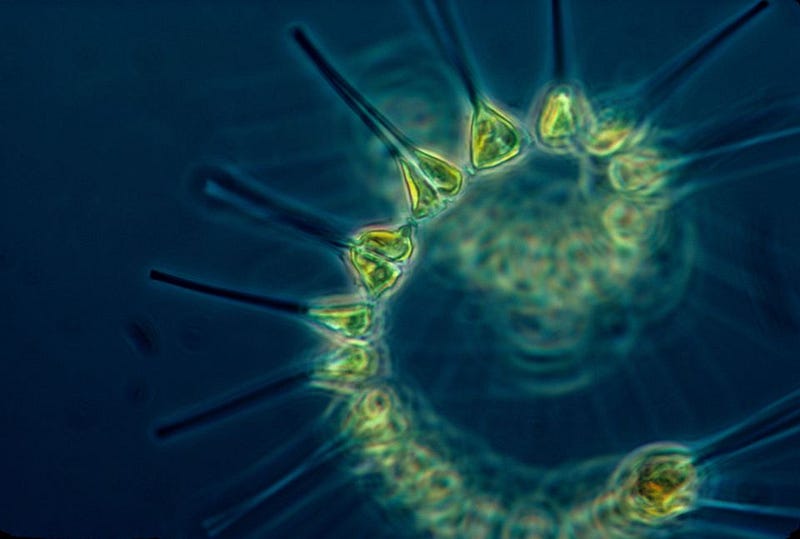
Photo by NOAA on Unsplash
Let’s examine the significance of plankton.
Phytoplankton are vital for oxygen production and carbon dioxide removal: Through photosynthesis, these organisms generate 50% of the Earth's oxygen while absorbing carbon dioxide from both the air and water.
They act as natural carbon sinks: Upon their demise, phytoplankton sink to the ocean floor, effectively sequestering carbon for thousands of years.
Plankton serve as the foundation of the marine ecosystem: Together with algae, phytoplankton constitute the primary producers within the ocean. They provide sustenance for zooplankton, which in turn feed various marine species, ranging from small fish to the largest whales. This intricate network forms the backbone of ocean life and directly impacts the health of marine food webs.
Producers are organisms that create their own food, serving as the fundamental basis of ecosystems. A healthy food web is characterized by a high population of producers, which diminishes as one moves up the food chain.
Plankton also affect cloud formation: When exposed to ultraviolet light stress, plankton emit a chemical known as DMSP, which bacteria break down into DMS. This compound is released into the atmosphere as tiny particles that facilitate cloud formation. These clouds shield the ocean from intense UV radiation, help regulate temperature, and protect marine flora.
Isn't it fascinating how nature operates so intelligently? Every element, no matter how small, has a purpose. However, human actions have unintentionally harmed plankton populations, leading to severe consequences.
Chapter 2: The Impact of Human Activity on Plankton
The first video, The Insanely Important World of Phytoplankton, dives into the crucial role these microorganisms play in our ecosystem.
The balance of nature is increasingly threatened by global warming. Natural processes produce carbon dioxide through respiration and decomposition, while plants and photosynthetic organisms absorb it during the day, creating a harmonious cycle.
Unfortunately, human activities, such as fossil fuel combustion and deforestation, have drastically increased carbon dioxide emissions. We are now releasing carbon dioxide faster than nature can absorb it!
This surplus of carbon dioxide traps heat in the atmosphere, resulting in warming oceans. Some of this gas dissolves in seawater, leading to ocean acidification. Scientists estimate a staggering 40% decline in phytoplankton since 1950 due to rising sea temperatures.
Additionally, warmer surface temperatures hinder the circulation of nutrient-rich water from the ocean's depths to the upper layers where phytoplankton thrive, making it increasingly difficult for them to acquire the necessary materials for photosynthesis.
Plastic pollution is another significant threat: Plankton, like many marine organisms, can confuse tiny plastic particles for food, particularly microfibers shed during laundry. Researchers have documented instances of plankton consuming microplastics, which adversely impacts their survival and reproductive capabilities.
The ingestion of plastic leads to bioaccumulation, spreading toxins throughout the marine food chain.
Nutrient pollution is equally harmful: Fertilizers from agricultural runoff introduce nitrogen and phosphorus into lakes and oceans, causing certain phytoplankton populations to explode, resulting in algal blooms. These blooms block sunlight and deplete oxygen in the water, creating dead zones that suffocate marine life.
When phytoplankton die, their decomposition further consumes oxygen, exacerbating the issue.
The repercussions of our actions are often unforeseen, especially for those of us who aren’t scientists. Understanding the critical roles played by plankton helps illuminate the dangers of their potential loss.
Chapter 3: Consequences of Plankton Decline
The second video, Tiny Desk Adventures: Diversity of Plankton - Micro vs Macro with Gabrielle Corradino, explores the various types of plankton and their essential functions within marine ecosystems.
The decline of plankton populations leads to several alarming consequences.
Reduced oxygen levels: As ocean temperatures rise and plankton numbers dwindle, there will be fewer phytoplankton available to produce oxygen. Simultaneously, increased carbon dioxide absorption will cause further ocean acidification, leading to a suffocating environment for marine life.
Accelerated global warming: Phytoplankton play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. Their decline means less carbon sequestration, leading to higher concentrations of greenhouse gases and exacerbating climate change.
Food shortages: A decrease in plankton disrupts the entire marine food web. Small fish and squids that rely on plankton for sustenance will face food scarcity, leading to diminished populations and cascading effects throughout the food chain. This will ultimately impact larger predators and wildlife, including sea birds and marine mammals, and threaten seafood supplies for human communities.
Bioaccumulation of toxins: Microplastics, often laden with harmful chemicals, pose a significant risk. When smaller fish consume contaminated plankton, toxins accumulate in their bodies. Larger fish that prey on these smaller species also retain these toxins, leading to greater concentrations higher up the food chain, which eventually can make their way onto our plates.
Despite their diminutive size, plankton are undeniably significant. They are essential for the survival of numerous marine species and, by extension, human beings. The loss of plankton would mean a drastic reduction in our oxygen supply, widespread starvation among marine life, and an acceleration of global warming.
Nonetheless, we are not powerless. By taking action now, we can make a difference. Here are some steps we can take to protect plankton:
- Minimize plastic usage: Avoid products containing microbeads, glitter, and synthetic fibers to reduce microplastic pollution.
- Conserve energy: Use public transportation to lower fossil fuel consumption.
- Be cautious with fertilizers: Prevent nutrient runoff into waterways to avoid algal blooms.
- Reduce meat consumption: As livestock farming contributes significantly to carbon emissions and deforestation, eating less meat can alleviate these pressures.
- Support conservation initiatives: Protecting natural habitats is crucial for preserving our planet's ecosystems and combating climate change.
- Educate others: Share information about the vital role of phytoplankton and the threats they face. Raising awareness is key to addressing these challenges.
If you, like me, previously overlooked the importance of these tiny organisms, I hope this information has been enlightening and has sparked your curiosity about plankton. They truly are some of the most undervalued organisms on our planet.
Please spread the word! The more we understand how our actions impact the environment, the better equipped we will be to tackle the climate crisis.
I’ve done my best to compile what I’ve learned about plankton. As I’m not a marine biologist, my explanations might not be flawless. If you notice any inaccuracies, I appreciate your understanding and feedback.