Exploring the Intersection of AI and Human Consciousness
Written on
Chapter 1: The AI Consciousness Debate
In recent discussions surrounding artificial intelligence, the question of whether AI can achieve consciousness has become a hot topic. What does it mean for AI to be sentient, or to possess a mind? This inquiry remains largely unanswered, as there is no consensus on what consciousness entails or how it manifests in humans. Philosophers and scientists continue to engage in vigorous debates on this subject. Claims by tech enthusiasts that current large-language-model chatbots are "conscious" or "alive" often miss the mark entirely.
However, a more focused question can be examined: under what circumstances do we humans perceive AI as having consciousness? What leads us to treat machines as if they possess a mind, and what are the consequences of this perception?
This line of questioning mirrors Alan Turing's approach in his formulation of the "Imitation Game," or the Turing Test. Turing proposed that if a chatbot can convincingly mimic human behavior, it can be considered a "thinking machine." Rather than seeking a definitive measure of consciousness, Turing suggested we observe how we relate to entities that appear to possess a mind.
To gain insight into this topic, I revisited a book I read in 2016, which offers valuable perspectives. The book, The Mind Club: Who Thinks, What Feels, and Why It Matters, authored by psychologists Daniel M. Wegner and Kurt Gray, delves into the field of "mind perception." It presents findings from a survey involving 2,499 participants tasked with evaluating the "mind" of various entities.

Chapter 2: Understanding Mind Perception
The authors introduced thirteen characters, including both humans and non-humans, to gauge how much "mind" respondents perceived in each. These ranged from an advertising executive to a sociable robot created at MIT. The human subjects were categorized as "minds," while non-human entities were labeled "cryptominds," indicating uncertainty about their mental capacity.
The researchers identified nineteen distinct mental abilities that might signify the presence of a mind, including reasoning, emotional recognition, and the capacity for pain or joy. They then asked participants to compare these characters based on their perceived mental abilities, leading to a total of 78 questions.
The analysis revealed that participants categorized mental abilities into two main groups: those related to "experience" and those related to "agency."
Section 2.1: Experience vs. Agency
The "experience" category encompasses the ability to have an inner life, including emotions like hunger, fear, and joy. It reflects what it feels like to have a mind. Conversely, the "agency" category pertains to mental abilities associated with action, such as planning and moral reasoning. The distinction between these two dimensions has significant implications for how we assign moral responsibility.
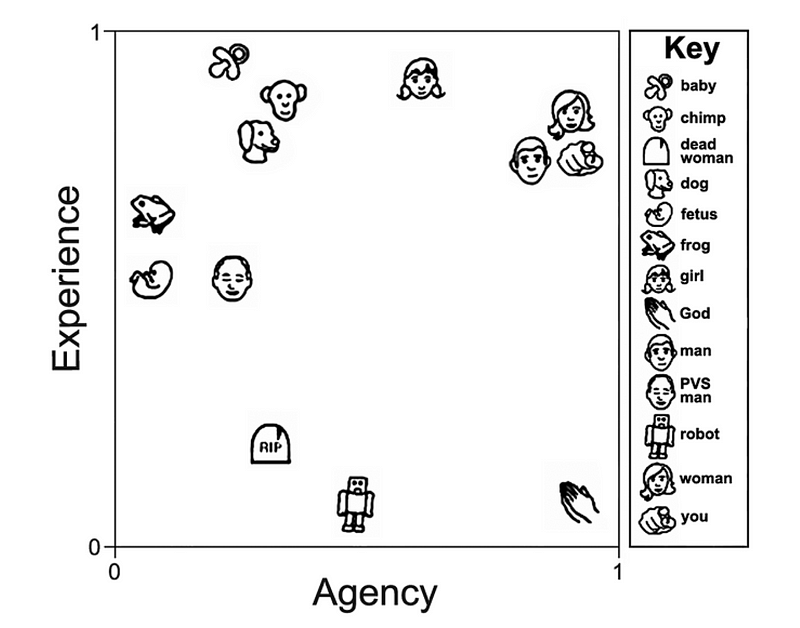
Subsection 2.1.1: The Moral Implications
The research indicates that entities perceived as possessing experience are often seen as deserving of moral rights, while those recognized for agency are viewed as having moral responsibilities. For instance, when posed with a moral dilemma involving a baby and a robot, respondents typically prioritized saving the baby, associating it with vulnerability and moral rights.
This distinction highlights a fundamental divide in how we perceive minds: on one side are "thinking doers," and on the other, "vulnerable feelers."
Chapter 3: AI in Society
The implications of this research resonate in contemporary discussions about self-driving cars. Advocates argue that these AI systems need real-world testing, while critics highlight the risks involved in using humans as test subjects for these machines. The experience/agency divide is evident in this debate, as critics view self-driving cars as high in agency but low in experience, thus assigning them moral responsibility for potential harm.
While it is true that human drivers are often unsafe, the moral weight of responsibility becomes more complex when considering that self-driving cars are designed and controlled by humans. If a robot car causes an accident, the accountability should not solely rest with the machine but also with its human creators.
Section 3.1: The Case of Blake Lemoine
Another relevant example is the case of Blake Lemoine, a former Google researcher who believed one of the company's AI systems exhibited signs of consciousness. Lemoine's interpretation of the AI's expressions of fear and vulnerability shifted its perception from an agency-focused robot to a more relatable, vulnerable entity akin to a child or pet.
Ultimately, The Mind Club provides a thought-provoking exploration of how we perceive minds and the moral implications of these perceptions. It invites readers to reflect on the evolving relationship between humans and machine intelligence in our daily lives.
(If you found this piece engaging, feel free to show your appreciation by clicking the clap button below. Each reader can offer up to 50 claps!)